IT-3-P-5736 Three-Dimensional Surface Modelling Of Cellular Structures And Intracellular Proteins Expression In Urinary Bladder Cancer Cells.
Introduction: Visualizing and describing structure and function at a subcellular level is of fundamental importance in the molecular pathological sciences. The majority of microscopic techniques give a single two-dimensional representation of often complex three-dimensional (3D) structures. In many cases it would be useful to be able to view objects seen under the microscope in three dimensions, an approach which has clear advantages for the user in terms of comprehension and interpretation.
The aim of this study: was to produce 3D models of data from confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) with a user-friendly PC software package. The study would examine the spatial localization of cellular proteins p53 and Bcl2 in apoptotic human urinary bladder cancer cell lines.
Material and method: Various combinations of immunofluorescence for the proteins of interest and propidium iodide staining for nuclear delineation were carried out in urinary bladder l cancer cells using contrasting fluorochromes. Specimens were examined with CLSM and stacks of optical sections from each light channel saved to disk. Using a desktop computer, the volumes of data were merged and rendered using gradient shading ray tracing. Surfaces of nuclei and protein aggregations were made transparent and the subcellular structures could be viewed from any angle. Series of renderings could be tagged together to produce a 3-D video moving sequences (build-up, fly-by and clipping) for better studying the protein expression.
In conclusion: the rendered images and videos were of high quality and were extremely helpful in studying the intracellular proteins expression. The technique both aided the research process and improved the means of scientific interpretation of gene and protein localization at the subcellular level.
the Author Thank Sarah Elkablawy, Ayah Elkablawy and Mona Mawlana for technical help and support. Also Thank dr. Nashaat Shawky for revising the language and grammer of the abstract.
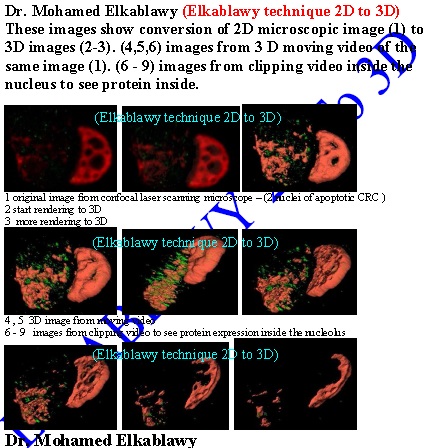
Fig. 1: this Images show the conversion of 2D image into series of 3D images |